Part 4: Debugging Checkout with Tracing
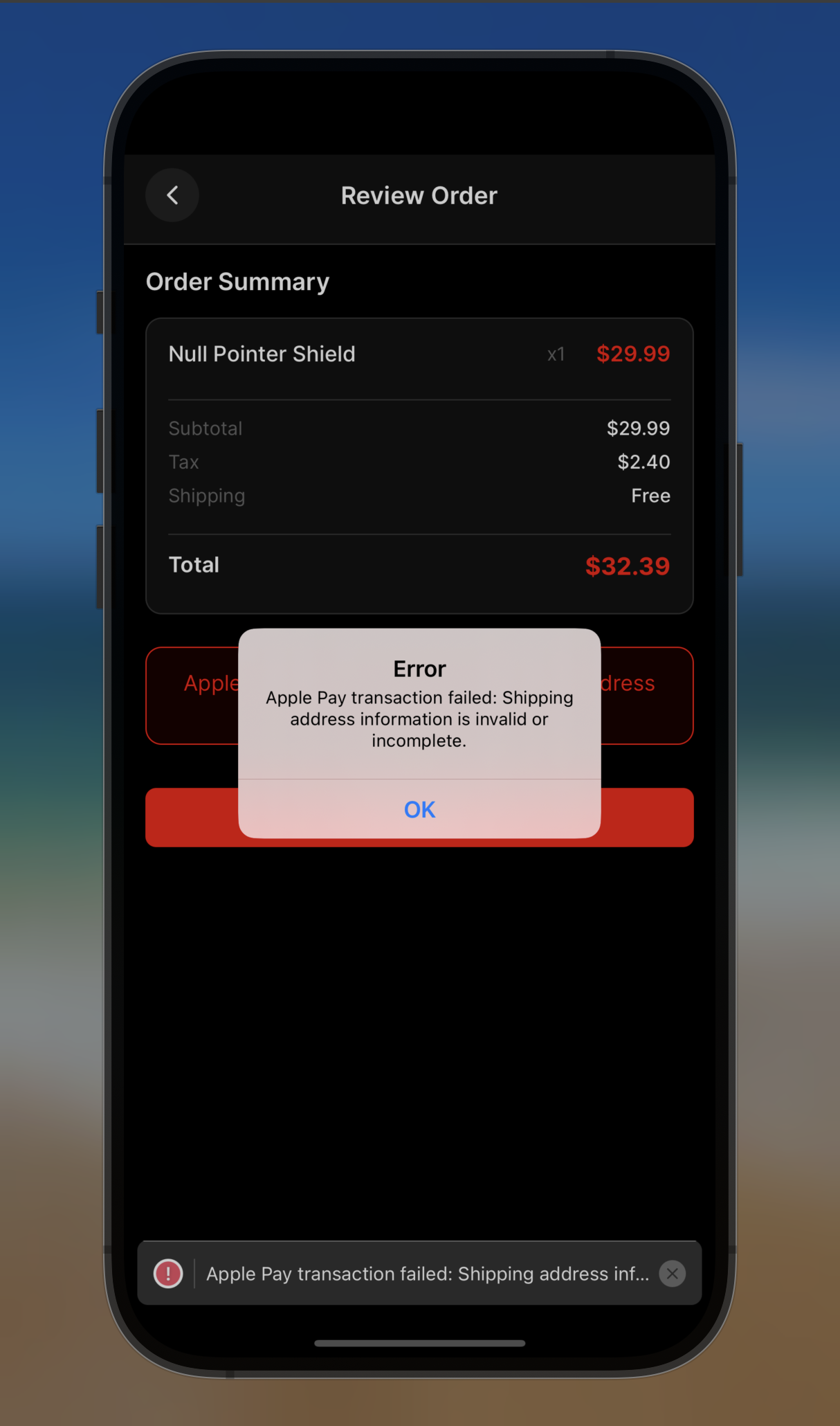
Now that we’ve fixed the cart issue and can successfully add items, let’s try to complete a purchase. When choosing Apple Pay as the payment method, customers encounter an error that prevents them from completing their transaction.
Examining the Error in Sentry
Let’s check Sentry to see what’s happening with this error:
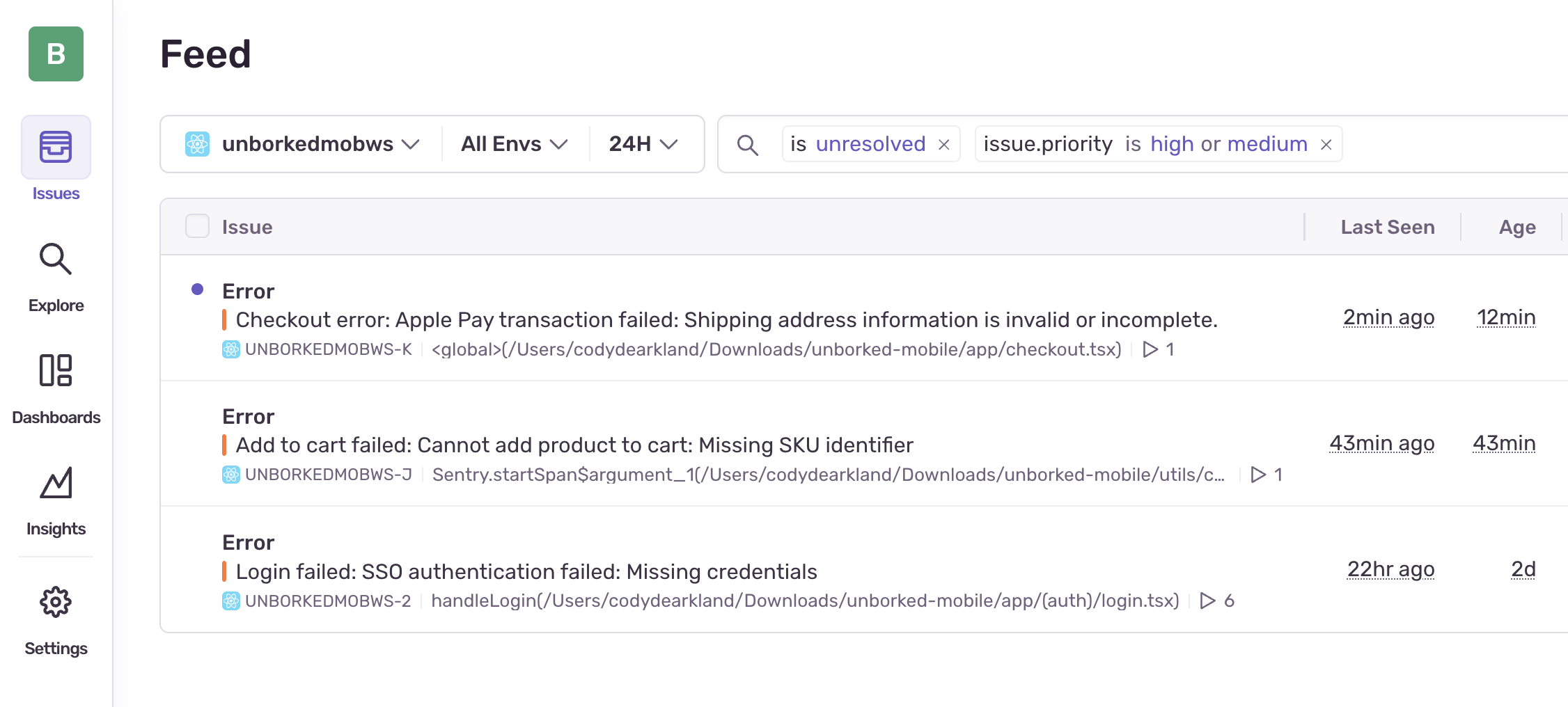
The error message indicates that the Apple Pay transaction is failing because of invalid or incomplete shipping address information. Let’s examine the details:
- Error Message: “Apple Pay transaction failed: Shipping address information is invalid or incomplete.”
- Stack Trace: Points to a problem in the PaymentService
- User Impact: Every customer attempting to use Apple Pay encounters this error
Using Tracing to Debug the Checkout Flow
Instead of just relying on error messages, let’s use Sentry’s tracing capabilities to visualize the entire checkout process and understand exactly where and why it’s failing.
Let’s first look at the payment flow. There are two key files to examine:
app/checkout.tsx- Contains the checkout UI and payment processservices/PaymentService.ts- Contains the payment processing logic
Adding Tracing to the Checkout Process
Let’s add tracing to our payment service to get better visibility into what’s happening:
// In services/PaymentService.tsimport * as Sentry from '@sentry/react-native';
// Update the processPayment method to include tracingstatic async processPayment( paymentMethodId: string, addressId: string | null, items: CartItem[], total: number): Promise<PaymentResult> { return Sentry.startSpan( { name: "processPayment" }, async (span) => { // Set payment information as span attributes span.setAttributes({ paymentMethodId, hasAddressId: addressId !== null, itemCount: items.length, total });
// Simulate network delay await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1500));
// Find selected payment method const paymentMethod = this.getPaymentMethodById(paymentMethodId);
if (!paymentMethod) { span.setAttributes({ paymentError: 'Payment method not found', paymentStatus: 'error' });
return { success: false, error: 'Payment method not found' }; }
// Add payment method details to span span.setAttributes({ paymentMethodType: paymentMethod.type, paymentMethodName: paymentMethod.name });
// Process payment based on type let result; switch (paymentMethod.type) { case 'card': result = await Sentry.startSpan( { name: "processCardPayment" }, async () => this.processCardPayment(paymentMethod, total) ); break; case 'paypal': result = await Sentry.startSpan( { name: "processPayPalPayment" }, async () => this.processPayPalPayment(total) ); break; case 'applepay': result = await Sentry.startSpan( { name: "processApplePayPayment" }, async (childSpan) => { childSpan.setAttributes({ addressId: addressId || 'null', total }); return this.processApplePayPayment(addressId, total); } ); break; default: span.setAttributes({ paymentError: 'Unsupported payment method', paymentStatus: 'error' });
result = { success: false, error: 'Unsupported payment method' }; }
// Add result to span span.setAttributes({ paymentSuccess: result.success, paymentError: result.error || 'none', transactionId: result.transactionId || 'none' });
return result; } );}Now, let’s update the Apple Pay processing method to use tracing:
/** * Process an Apple Pay payment with tracing */private static processApplePayPayment( addressId: string | null, total: number, parentSpan: Sentry.Span): PaymentResult { // Apple Pay requires a shipping address to process the payment
if (addressId === null) { parentSpan.setAttributes({ paymentError: 'Shipping address is required for Apple Pay', paymentStatus: 'error' });
const error = new Error('Shipping address is required for Apple Pay'); console.error(error); throw error; }
// Trace the address lookup return Sentry.startSpan( { name: "fetchAddressForApplePay" }, (span) => { span.setAttributes({ addressId, action: 'address_lookup' });
// BROKEN: Even if addressId is provided, we're not fetching or using the actual address details // The Apple Pay API requires the complete address object, not just the ID
try { // Try to get the address but don't use it const address = this.getAddressById(addressId);
// Record if we found the address span.setAttributes({ addressFound: address !== undefined, addressCity: address?.city || 'unknown', addressComplete: address !== undefined });
// Instead, we'll just throw an error that looks like it came from Apple Pay const addressError = new Error('Apple Pay transaction failed: Shipping address information is invalid or incomplete.'); console.error(addressError);
span.setAttributes({ paymentError: 'Address information not used in payment processing', paymentStatus: 'error' });
throw addressError; } catch (error: any) { span.setAttributes({ paymentError: error.message, paymentStatus: 'error' });
throw error; } } );
// WORKING VERSION (uncomment to fix): // return Sentry.startSpan( // { name: "fetchAddressForApplePay" }, // (span) => { // span.setAttributes({ // addressId, // action: 'address_lookup' // }); // // // Fetch the full address // const address = this.getAddressById(addressId); // // // Make sure the address exists // if (!address) { // span.setStatus({ // code: Sentry.SpanStatusType.ERROR, // message: 'Invalid shipping address' // }); // // return { // success: false, // error: 'Invalid shipping address' // }; // } // // // Record that we found and are using the address // span.setAttributes({ // addressFound: true, // addressCity: address.city, // addressComplete: true, // addressUsed: true // }); // // // Success! // return { // success: true, // transactionId: `applepay-${Date.now()}` // }; // } // );}Analyzing the Trace in Sentry
After adding tracing and reproducing the error, we can examine the trace in Sentry.
The error is showing up, and we can search for the Trace by navigating to the “Tracing” tab under “Explore” on the left, and using the Trace Explorer to find the trace. We can use the text field to search for the name or span operation.
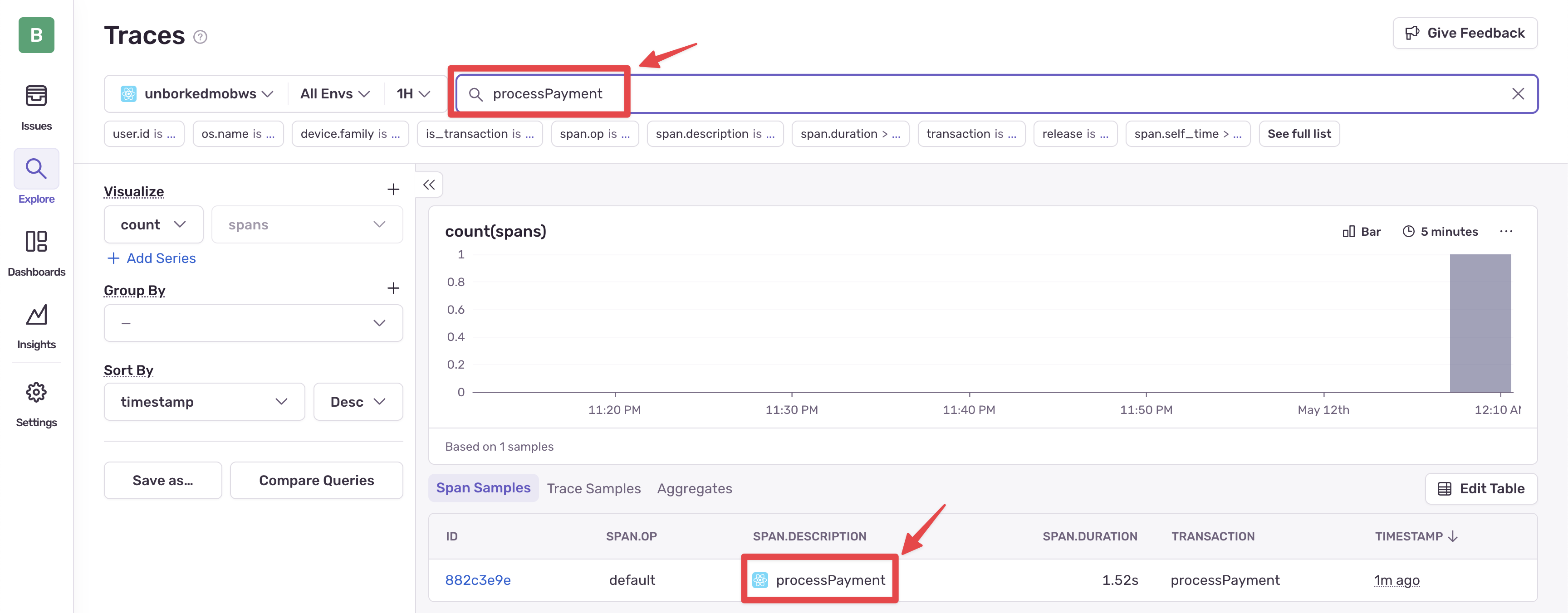
Once we find it, we can click into the trace and explore its details.
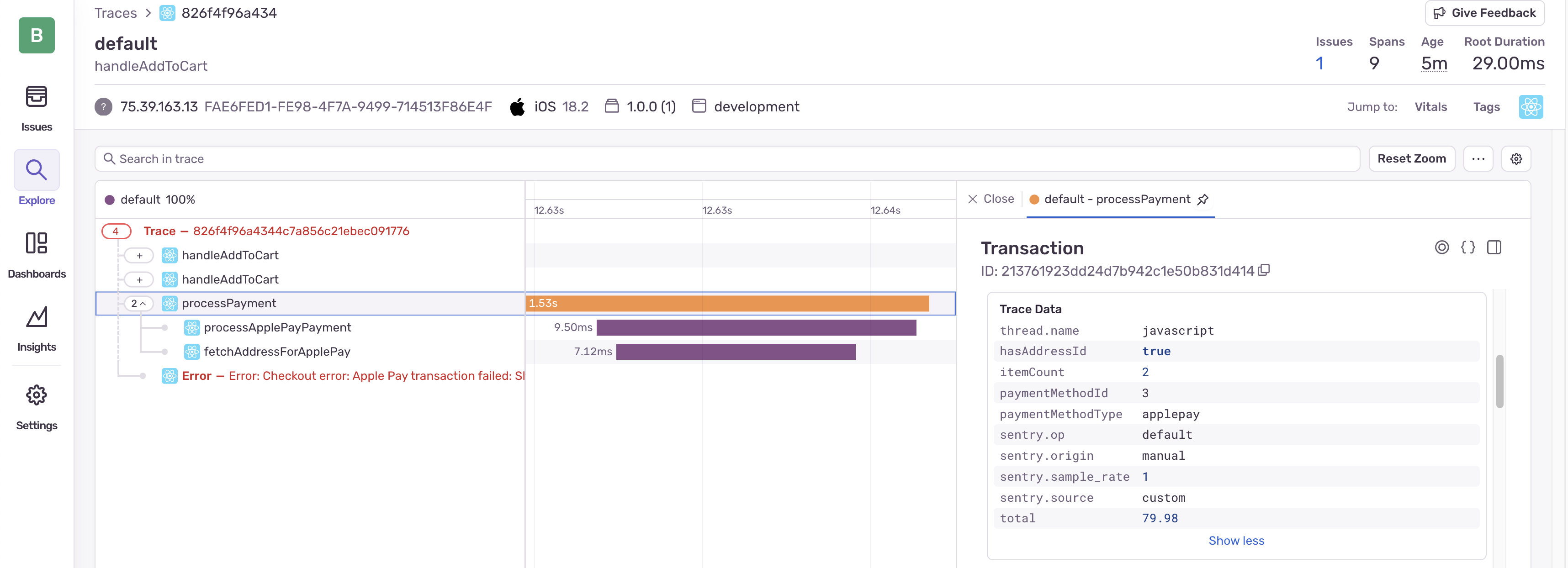
How to Analyze the Payment Trace
Let’s examine the trace to understand what’s happening:
-
Identify the main transaction: The
processPaymentspan shows the entire payment flow. -
Examine the span hierarchy: Note how the flow branches from
processPaymenttoprocessApplePayPaymentand then tofetchAddressForApplePay. -
Check span attributes: Click on each span to view its attributes:
- In the
processPaymentspan, we can see the payment method is “applepay” and there’s an addressId
- In the
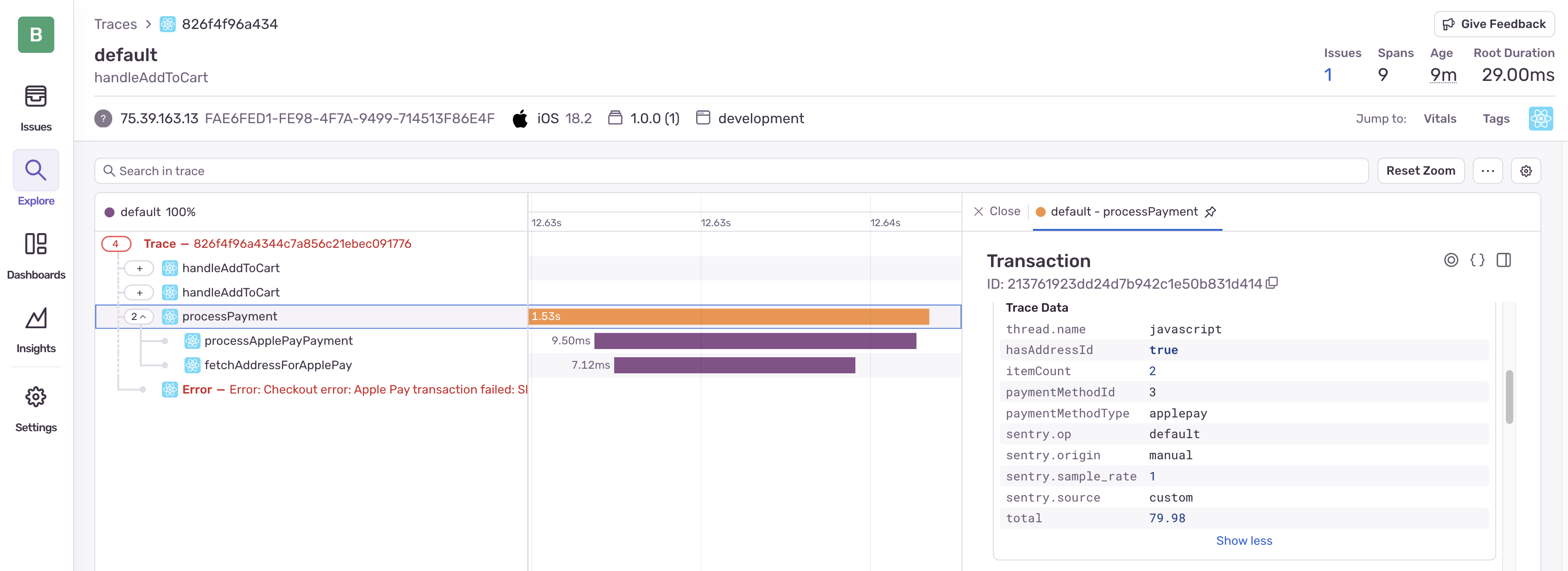
- In the
fetchAddressForApplePayspan, we can see if the address was found.
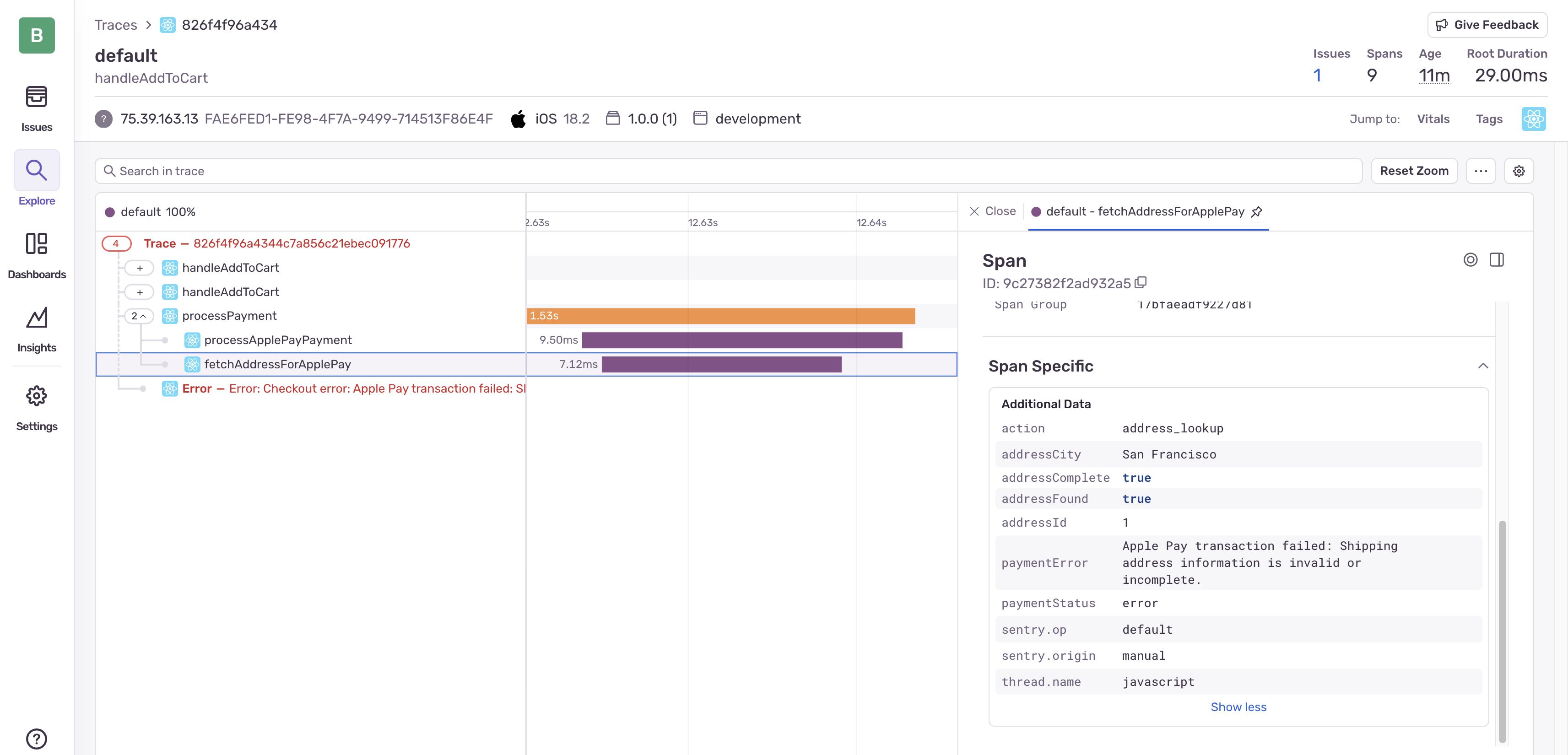
- Look for error attributes: The
fetchAddressForApplePayspan has attributes indicating an error with the message “Address information not used in payment processing”
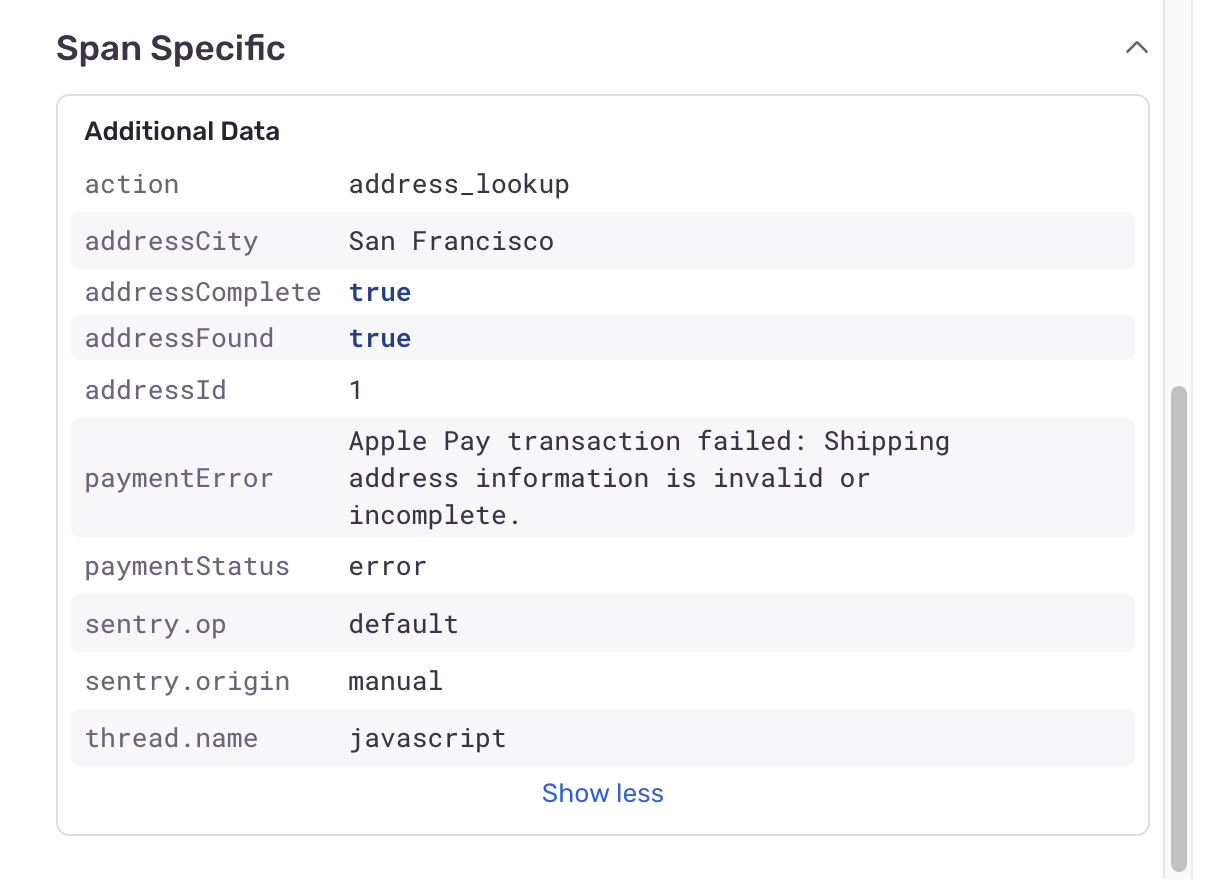
- Follow the error flow: Notice how errors are captured as attributes in each span, showing how the error propagates through the system
What the Trace Reveals
The trace clearly shows:
- The address ID is provided to the payment method
- The address is successfully found in our database (addressFound: true)
- But the Apple Pay processor isn’t actually using the address information
- This results in the “invalid or incomplete” shipping address error
This visualization helps us understand that the issue isn’t with missing data, but with how the data is (or isn’t) being used in the processing flow.
Fixing the Issue
Based on our trace analysis, we need to modify the processApplePayPayment method to actually use the address that it successfully looks up:
/** * Process an Apple Pay payment with tracing */private static processApplePayPayment( addressId: string | null, total: number, parentSpan: Sentry.Span): PaymentResult { // Apple Pay requires a shipping address to process the payment
if (addressId === null) { parentSpan.setAttributes({ paymentError: 'Shipping address is required for Apple Pay', paymentStatus: 'error' });
return { success: false, error: 'Shipping address is required for Apple Pay' }; }
return Sentry.startSpan( { name: "fetchAddressForApplePay" }, (span) => { span.setAttributes({ addressId, action: 'address_lookup' });
// Fetch the full address const address = this.getAddressById(addressId);
// Make sure the address exists if (!address) { span.setAttributes({ paymentError: 'Invalid shipping address', paymentStatus: 'error' });
return { success: false, error: 'Invalid shipping address' }; }
// Record that we found and are using the address span.setAttributes({ addressFound: true, addressCity: address.city, addressComplete: true, addressUsed: true });
// In a real app, we would use the address details to create a payload // and send it to the Apple Pay API
// Success! return { success: true, transactionId: `applepay-${Date.now()}` }; } );}Let’s make this change to fix the issue:
- Open
services/PaymentService.ts - Find the
processApplePayPaymentmethod - Replace the broken code with the working version that uses the address
After making this change, let’s try checking out with Apple Pay again:
Viewing the Successful Trace
After fixing the issue, let’s look at the successful payment trace:
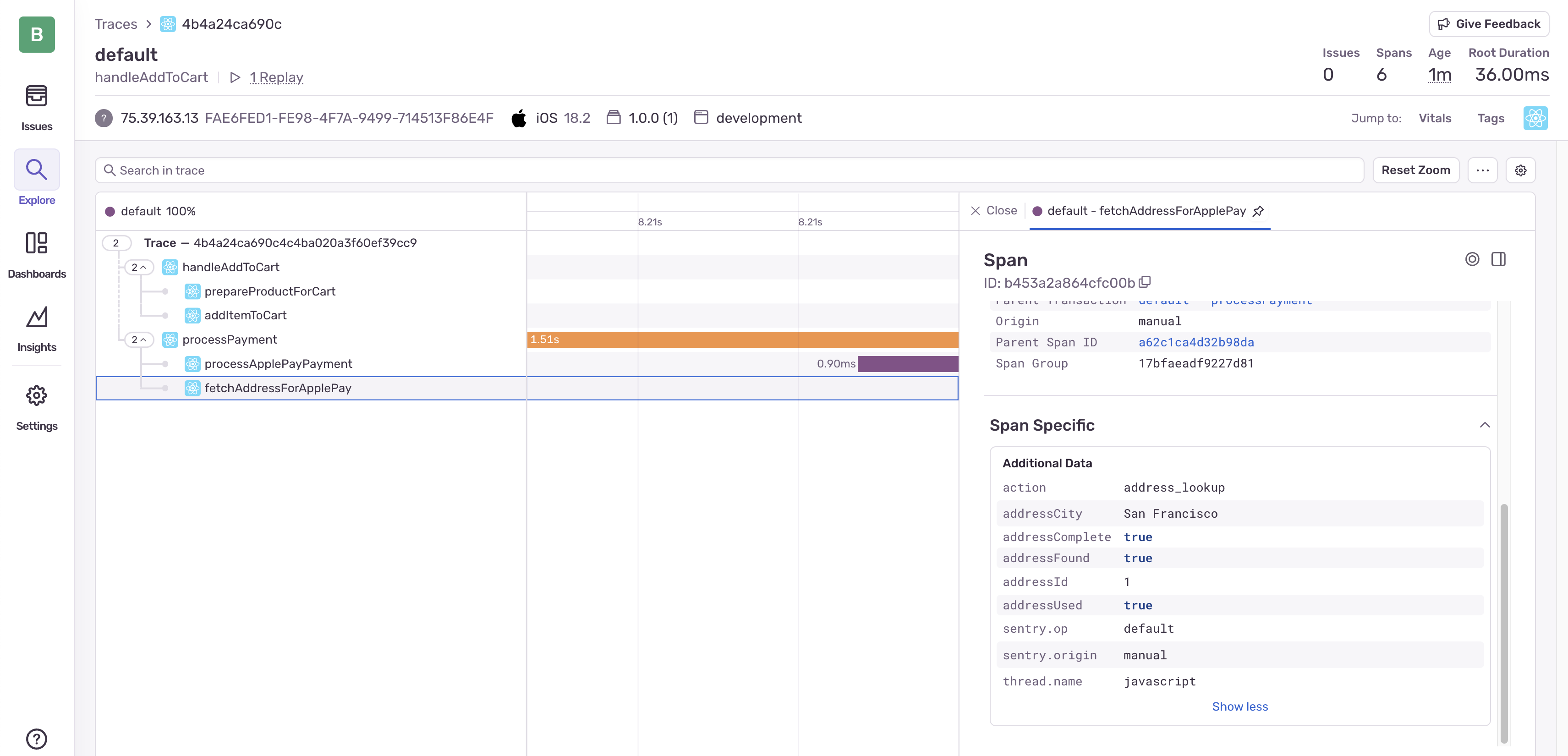
Notice how all spans complete successfully, and the attributes show that the address was both found and used in the payment process.
What We Learned
Using tracing for our payment debugging provided several key insights:
-
Visualizing the Entire Process: Tracing showed us the complete payment flow, not just where it failed.
-
Data Flow Visibility: We could see that the address was successfully fetched but not used in the payment processing.
-
Context Through Attributes: Span attributes provided rich context about what data was available at each step.
-
Error Propagation: We could see how errors propagated up through the span hierarchy.
-
Process Validation: After fixing the issue, tracing confirmed our entire payment flow was working correctly.
Best Practices for Payment Processing with Tracing
When implementing payment processing with tracing:
-
Trace the Entire Flow: Create a parent span for the whole payment process and child spans for each step.
-
Add Meaningful Attributes: Include relevant data as span attributes at each stage.
-
Set Appropriate Status: Use status codes to indicate success or failure states.
-
Verify Data Availability: Use attributes to confirm required data is available throughout the process.
-
Compare Before and After: Compare traces before and after fixes to validate improvements.
Tracing is particularly valuable for payment systems because it visualizes the entire flow of data through complex, multi-step processes, making it easier to spot exactly where things go wrong.
Now that we’ve fixed the checkout flow, customers can successfully complete their purchases using Apple Pay, improving their shopping experience and increasing conversion rates for the store.